As a car owner, there’s nothing more frustrating than seeing that dreaded “Check Engine” light illuminate on your dashboard. It’s like your car is trying to tell you something, but you’re not quite sure what it’s saying. That’s where On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) trouble codes come in – a standardized system that helps you diagnose and fix problems with your vehicle.
In this article, we’ll break down how to interpret OBD trouble codes, step by step. We’ll cover what they are, how to retrieve them, and what they mean. By the end of this guide, you’ll be empowered to tackle common car issues like a pro, saving you time, money, and stress in the process.
What are OBD Trouble Codes?
OBD trouble codes are a series of alphanumeric codes that your car’s onboard computer generates when it detects a problem. These codes are standardized across all vehicles manufactured since 1996, making it easier for mechanics and DIY enthusiasts alike to diagnose issues.
Think of OBD codes like a secret language that your car uses to communicate with you. They’re usually a combination of letters and numbers that correspond to a specific problem or system malfunction. For example, the code “P0123” might indicate a problem with your car’s oxygen sensor, while “U0100” could signal a communication issue between your car’s computer and a sensor.
How to Retrieve OBD Trouble Codes
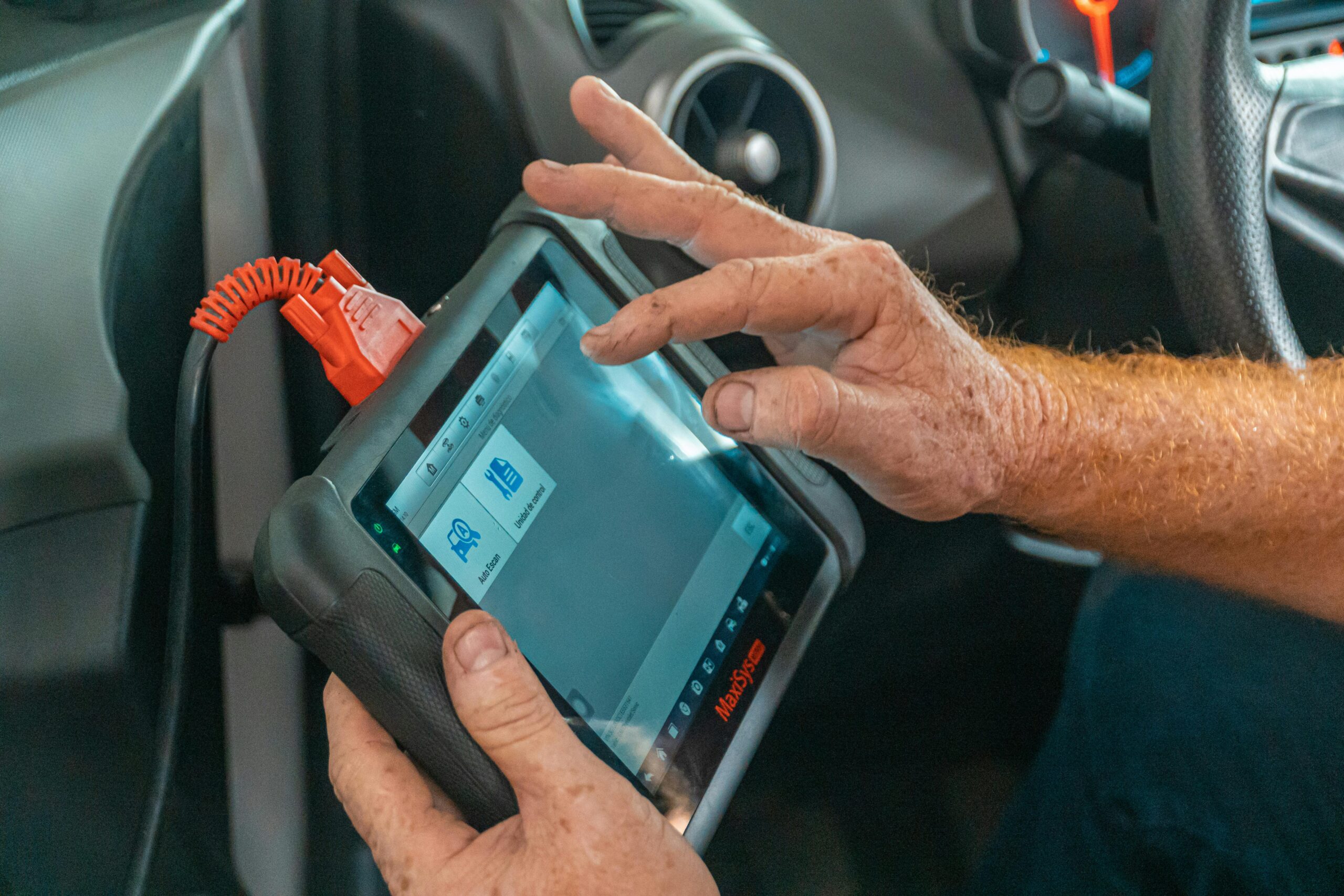
Retrieving OBD trouble codes is relatively straightforward. You’ll need a few tools and some basic knowledge of your car’s systems. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Purchase an OBD-II Scanner: You can buy an OBD-II scanner at most auto parts stores or online. These scanners plug into your car’s OBD-II port (usually located under the steering column) and display the trouble codes on a screen.
- Locate the OBD-II Port: Check your car’s manual or look for a label on the driver’s side dashboard or under the steering column. The port is usually a trapezoidal-shaped connector with a plastic cover.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD-II scanner to the port and turn the ignition to the “on” position (but don’t start the engine).
- Retrieve the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve the trouble codes. This might involve pressing a button or navigating through a menu.
- Write Down the Codes: Record the codes displayed on the scanner’s screen. You might need to refer to them later.
Interpreting OBD Trouble Codes
Now that you have the codes, it’s time to interpret them. Here’s a breakdown of how to read and understand OBD trouble codes:
- Code Structure: OBD trouble codes usually consist of a letter and four numbers (e.g., P0123). The letter indicates the system or category affected, while the numbers specify the problem.
- System Codes: The first letter or character of the code indicates the system affected:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, etc.)
- B: Body (lights, wipers, etc.)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension, etc.)
- U: Network/Communication (computer, sensors, etc.)
- Problem Codes: The numbers following the letter indicate the specific problem. For example:
- P0123: Oxygen sensor circuit malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- U0100: Lost communication with a sensor or module
Common OBD Trouble Codes
Here are some common OBD trouble codes you might encounter:
- P0123: Oxygen sensor circuit malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0171: System too lean (Bank 1)
- P0420: Catalyst system efficiency below threshold (Bank 1)
- U0100: Lost communication with a sensor or module
- B1205: Driver’s side airbag module fault
What to Do Next
Once you’ve interpreted the OBD trouble code, it’s time to take action:
- Consult Your Owner’s Manual: Check your car’s manual for guidance on troubleshooting and repairing common issues.
- Research Online: Websites like Autozone, O’Reilly Auto Parts, or YouTube can provide valuable resources and tutorials.
- Visit a Mechanic: If you’re not comfortable DIY-ing the repair or need further assistance, take your car to a trusted mechanic.
- Clear the Code: Once you’ve fixed the issue, use your OBD-II scanner to clear the trouble code from your car’s computer.
Potential Pitfalls to Avoid
When working with OBD trouble codes, keep the following in mind:
- Don’t Ignore the Problem: Failing to address the issue can lead to further damage, decreased fuel efficiency, or even safety hazards.
- Don’t Overlook Other Codes: Make sure to retrieve and address all trouble codes, as multiple issues might be related or interconnected.
- Don’t Rely Solely on the Code: OBD trouble codes are just a starting point. Always perform a thorough diagnosis and inspection to ensure you’re addressing the root cause of the problem.
Conclusion
Interpreting OBD trouble codes is a valuable skill that can save you time, money, and stress. By understanding how to retrieve and interpret these codes, you’ll be better equipped to diagnose and fix common car issues. Remember to stay vigilant, do your research, and seek professional help when needed. With practice and patience, you’ll become a master of OBD trouble codes and keep your car running smoothly for years to come.
Helpful Resources
- OBD-Codes.com: A comprehensive database of OBD trouble codes, including explanations and repair guides.
- Autozone.com: A leading auto parts retailer offering OBD-II scanners, repair guides, and DIY tutorials.
- YouTube: A wealth of DIY repair videos and tutorials covering various car models and OBD trouble codes.
By following these steps and resources, you’ll be well on your way to becoming an OBD trouble code expert. Happy diagnosing!























































Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.