As a car owner, it’s essential to stay on top of your vehicle’s maintenance to avoid costly repairs and ensure a safe driving experience. One of the most critical systems to monitor is your engine, which can exhibit various performance symptoms that may indicate underlying issues. In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of diagnosing common engine performance symptoms, helping you identify potential problems and take corrective action.
Symptom 1: Loss of Power or Sluggish Acceleration
If your car is struggling to accelerate or lacks power when driving, it may be due to several reasons. Here are some possible causes:
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Worn-out spark plugs can lead to misfires, reducing engine performance. Check your spark plugs and replace them if necessary.
- Clogged Air Filter: A dirty or clogged air filter can restrict airflow, resulting in decreased engine power. Inspect and clean or replace your air filter as needed.
- Low Fuel Pressure: Low fuel pressure can cause your engine to run lean, leading to a loss of power. Check your fuel pressure gauge to ensure it’s within the recommended range.
Symptom 2: Engine Stalling or Hesitation
If your engine stalls or hesitates when driving, it may be due to:
- Faulty Fuel Injectors: Clogged or dirty fuel injectors can cause your engine to stall or hesitate. Clean or replace your fuel injectors if necessary.
- Ignition System Issues: Problems with your ignition system, such as a faulty ignition coil or spark plug wires, can cause engine stalling. Inspect your ignition system and replace any faulty components.
- Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks can cause your engine to stall or hesitate. Check your intake manifold and vacuum hoses for any signs of leaks.
Symptom 3: Engine Knocking or Pinging
If you hear knocking or pinging sounds from your engine, it may be due to:
- Low-Octane Fuel: Using low-octane fuel can cause engine knocking or pinging. Ensure you’re using the recommended fuel type for your vehicle.
- Ignition Timing Issues: Problems with your ignition timing can cause engine knocking or pinging. Check your ignition timing and adjust it if necessary.
- Carbon Buildup: Carbon buildup on your engine’s cylinder walls can cause knocking or pinging sounds. Consider using a fuel additive to help clean your engine.
Symptom 4: Increased Fuel Consumption
If you’ve noticed a sudden increase in fuel consumption, it may be due to:
- Clogged Fuel Injectors: Dirty or clogged fuel injectors can cause your engine to run rich, leading to increased fuel consumption. Clean or replace your fuel injectors if necessary.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: A faulty oxygen sensor can cause your engine to run rich, resulting in increased fuel consumption. Replace your oxygen sensor if it’s faulty.
- Low Tire Pressure: Underinflated tires can increase rolling resistance, leading to higher fuel consumption. Check your tire pressure regularly and maintain the recommended level.
Symptom 5: Engine Overheating
If your engine is overheating, it may be due to:
- Coolant Leaks: Coolant leaks can cause your engine to overheat. Inspect your cooling system for any signs of leaks.
- Faulty Radiator Fan: A faulty radiator fan can cause your engine to overheat. Check your radiator fan and replace it if necessary.
- Clogged Radiator: A clogged radiator can restrict coolant flow, leading to engine overheating. Clean or replace your radiator if necessary.
Diagnosing Engine Performance Symptoms: A Step-by-Step Approach
To diagnose engine performance symptoms, follow these steps:
- Gather Information: Take note of the symptoms you’re experiencing, including when they occur and any error codes displayed on your dashboard.
- Consult Your Owner’s Manual: Refer to your owner’s manual for guidance on troubleshooting engine performance issues.
- Perform a Visual Inspection: Inspect your engine and its components for any signs of damage, wear, or leaks.
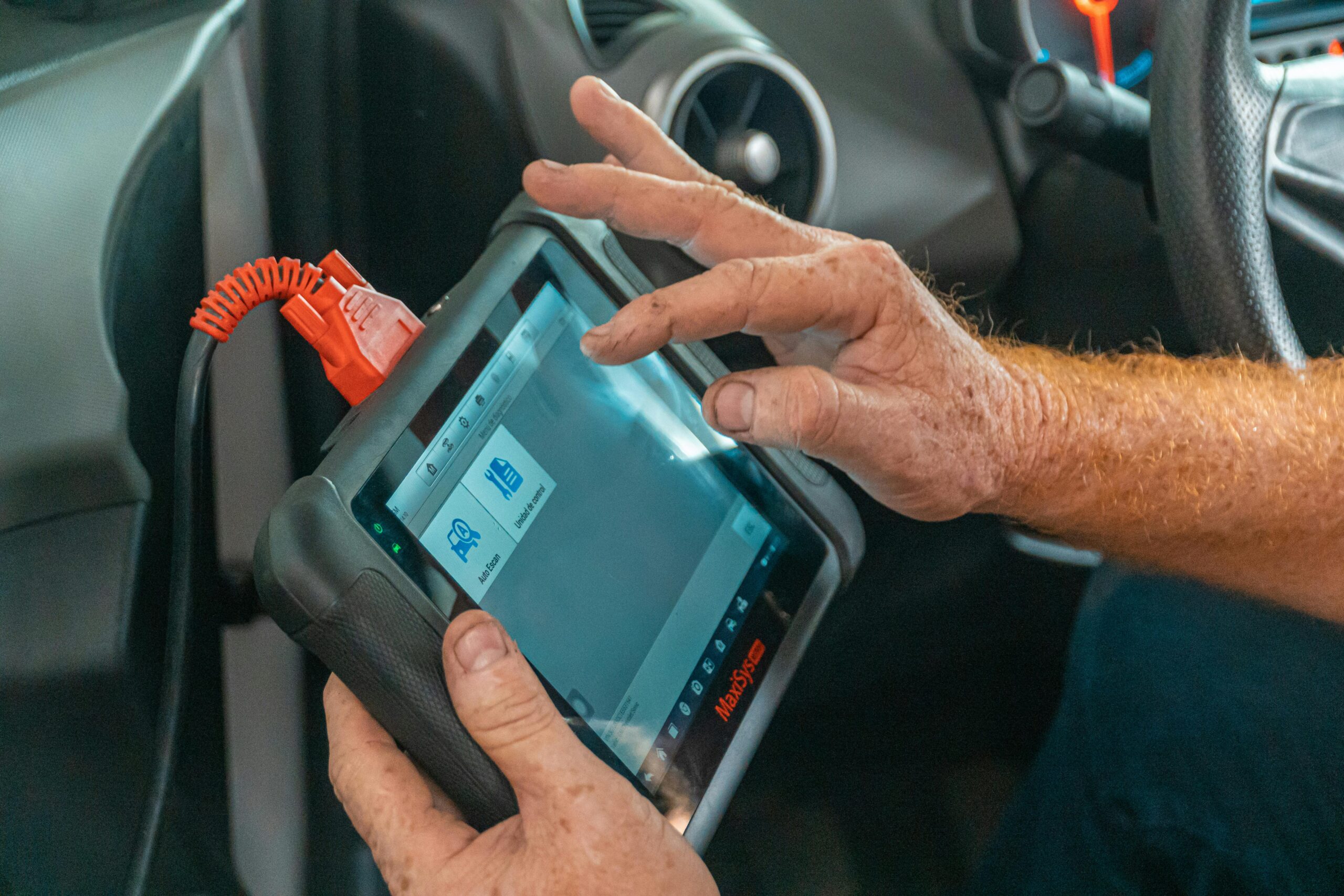
- Use Diagnostic Tools: Utilize diagnostic tools, such as a code reader or scan tool, to retrieve error codes and monitor engine performance.
- Test and Replace Components: Test and replace any faulty components, following the manufacturer’s recommended procedures.
Conclusion
Diagnosing common engine performance symptoms requires a systematic approach, patience, and attention to detail. By following the steps outlined in this article, you’ll be better equipped to identify potential issues and take corrective action, saving you money and ensuring a safe driving experience. Remember to stay on top of your vehicle’s maintenance, and don’t hesitate to seek professional help if you’re unsure about diagnosing or repairing engine performance issues.























































Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.